Ozone is a chemical compound consisting of three oxygen atoms O3 (ie triatomic oxygen), a highly energetic form of normal (diatomic) atmospheric oxygen (O2). Thus, the molecules of these two forms are different in structure. Due to its being an extremely powerful oxidizing agent and a highly effective disinfectant, it is used throughout the world to destroy germs in water treatment installations supplying drinking water.
Ozone therapy
- Home
- Ozone therapy
- Local Hyperthermia as a major tool in treating Cancer patients successfully in a non-toxic way
- Why are IQ scores declining over the previous 20 years?
- Expert report regarding the clinical use of CBD
- CBD effective in Healing Bone Fractures at all Ages and Prevention and Cure of Osteoporosis and Arthrosis
- Medical Cannabis Approval Sweeps Across Europe
- More people die from overdosing on pharmaceutical drugs than illegal drugs
- Flu vaccine BOMBSHELL: 630% more “aerosolized flu virus particles” emitted by people who received flu shots… flu vaccines actually SPREAD the flu
Ozone therapy - What is ozone?
What is ozone therapy?
Medical ozone is always a mixture of purest ozone and purest oxygen. According to its application, the ozone concentration can vary between 1 and 100 µg/ml (0.05 – 5 % O3). The ozone therapist, a trained physician, determines the complete dosage according to the medical indication and the patient’s condition.
Information provided by the Medical Society for Ozone application in Prevention and Therapy – www.ozone-association.com
-
In what diseases is ozone therapy usually applied ?
A whole number of pathological conditions exist which can be influenced positively or even healed by ozone. This is a fact which has been confirmed by a wide series of scientific investigations and medical publications. As a rule, medical ozone is applied in addition to other therapeutic methods ie it belongs to the field of complementary medicine. For all patients, men and women, to know about the latest developments in ozone therapy – and as quickly as possible – a large number of therapists (in Europe) got together and founded the (legally registered) Medical Society for Ozone Application in Prevention and Therapy, formerly called the Medical Society for Ozone Therapy, with the aim of providing basic information to doctors/therapists and patients alike. As to how far your physician is able to inform and help you depends on the country you are in and the current status of medical ozone. All should know, however, that medical ozone, when properly and responsibly handled (and the correct indication has been established), is safe, practical, effective and – as a preventive at least – low in cost. Naturally, in spite of this , as with all other forms of medical treatment, no 100 % guarantee can be given that ozone therapy will alleviate the condition it has been applied for. Success will vary according to the patient’s state of health, the frequency of ozone treatment, the doses and concentrations applied, and a number of other factor.
- Circulatory disorders
- Regeneration and revitalisation
- The elderly patient. Prevention and therapy
- Diseases of the eye
- Malignant disease (cancer)
- Fungal skin infections and infected skin lesions
- Infected wounds
- Intestinal diseases: proctitis and colitis
- Viral diseases
- Herpes simplex (facial herpes), herpes zoster (shingles)
- Inflammatory processes of the liver
- Inflammatory and degenerative joint conditions
- Arthritic/rheumatic conditions
- Chronic polyarthritis
-
Effects and medical uses
Activation of red blood cell metabolism improved oxygen supply. Activation of immune cells the body releases is own vital cytokins, such as interferones and interleukins. Increase and activation of the body’s own antioxidants and radical scavengers.
Medical uses:
- arterial circulatory disorders (peripheral and cerebral in particular);
- revitalization;
- omplementary therapy in various kinds of cancer;
- general immune weakness;
- inflammatory processes, eg arthritis, reactivated;
- arthrosis, vascular conditions;
- age-related processes.
-
What should I know as a patient ?
Before undergoing any form of ozone therapy, you should inform your doctor about any medication or special dietary measures you are taking or have been taking recently. You should only discontinue a regimen of this kind if your doctor advises you to do so. He or she should also know about allergies, inherited diseases or other complaints, and how they have been treated.
In many countries, especially outside Europe, ozone therapy is not always covered by health insurance policies or employers’ medical benefit schemes. You should also try to find out where ozone units exist in your country, what trained specialists are available, and how much treatment costs. Most ozone applications are in series of up to 10 sessions, and a second or even third series may be necessary in some indications.
Nevertheless, you should always remember that a little prevention can save a much more expensive full-scale treatment later on. Ozone therapy is low risk and usually applied as a complementary, additive or restorative method, ie in accompaniment of standard medical treatments.
Properties and effect of the ozone therapy
Medical ozone has highly pronounced bactericidal, fungicidal and virostatic properties, and is thus widely used in disinfecting infected wounds, as well as in bacterially and virally produced diseases. Its ability to stimulate the circulation is used in the treatment of circulatory disorders and makes it valuable in revitalizing organic functions. When administered at low concentrations, the organism’s own resistance is mobilized, ie ozone (re)activates the immune system.
As a response to this activation through ozone, the body’s immune cells produce special messengers called cytokins (including important mediators such as interferones or interleukins). These inform other immune cells, setting off a cascade of positive changes throughout the immune system, which is stimulated to resist diseases for example. This means that the application of medical ozone is extremely useful for immune activation in patients with a low immune status and/or immune deficit.
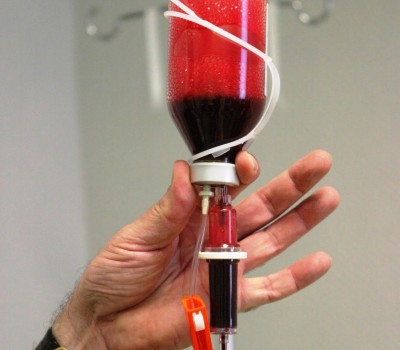
Small quantities of ozone applied in what is called “major autohemotherapy” (external treatment of the patient’s blood before reinfusion) consequently activate the body’s own antioxidants and radical scavengers. It is thus possible to understand why ozone is used in diseases which involve chronic inflammation. Thanks to its selective properties, medical ozone is used in three principal fields of indication:
- The treatment of circulatory disorders, also in the field of geriatrics;
- The treatment of diseases produced by viruses such as liver diseases (hepatitis) and herpes;
- The treatment of infected, badly healing wounds and inflammatory processes, such as for example:
- Open ulcers on the legs (ulcus cruris);
- Inflammatory intestinal conditions (Colitis, Proktitis);
- Burns, scalds and infected wounds, fungus infections and others;
- As an additive or complementary therapy in various types of cancer, ozone is applied for general immunoactivation at low dosages in the form of “major autohemotherapy” (reinfusion) or “minor autohemotherapy” (reinjection) via the intramuscular route.


 Deutsch
Deutsch Nederlands
Nederlands Turkish
Turkish Russian
Russian Italiano
Italiano Français
Français Português
Português العربية
العربية